It has been discovered that GootBot, a new GootLoader malware variant, makes it easier for compromised systems to move laterally and avoid detection.
According to IBM X-Force experts Golo Mühr and Ole Villadsen, “the GootLoader group’s introduction of their own custom bot into the late stages of their attack chain is an attempt to avoid detections when using off-the-shelf tools for C2 such as CobaltStrike or RDP.”
“This new variant is a lightweight but effective malware allowing attackers to rapidly spread throughout the network and deploy further payloads.”
As its name suggests, GootLoader is a malware that can lure in potential victims by employing search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning techniques, and once inside, it can download more sophisticated malware. It is connected to a threat actor known as UNC2565, also tagged as Hive0127.
The usage of GootBot suggests a change in strategy from post-exploitation frameworks like CobaltStrike, with the implant being downloaded as a payload following a Gootloader infection.”
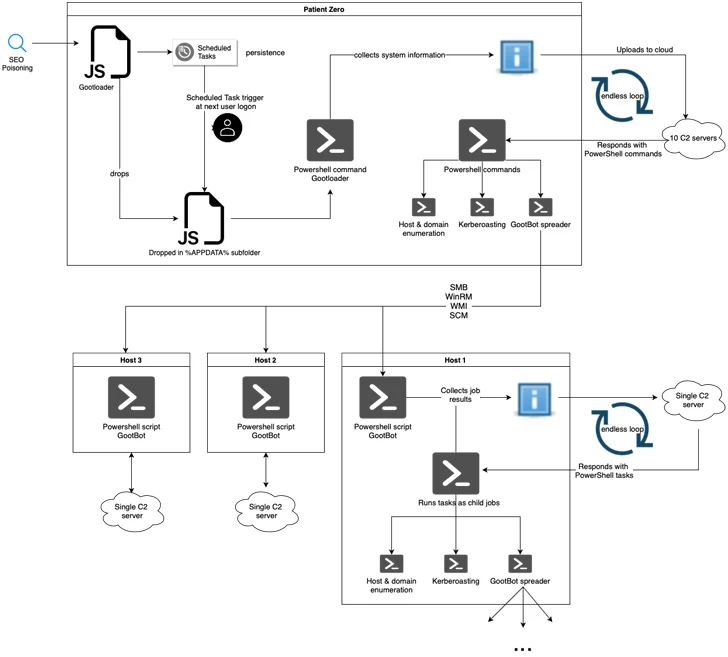
GootBot, which is described as an obfuscated PowerShell script, is made to connect to a WordPress website that has been compromised in order to take control of it and issue commands.
The usage of a different hard-coded C2 server for every deposited GootBot sample complicates matters even more and makes it challenging to stop malicious traffic.
“Currently observed campaigns leverage SEO-poisoned searches for themes such as contracts, legal forms, or other business-related documents, directing victims to compromised sites designed to look like legitimate forums where they are tricked into downloading the initial payload as an archive file,” the investigators stated.
To achieve persistence, the archive file includes an obfuscated JavaScript file that, when executed, retrieves another JavaScript file that is activated by a scheduled task.
The second stage involves the engineering of JavaScript to execute a PowerShell script that collects system information and exfiltrates it to a remote server. The server then answers with another PowerShell script that runs indefinitely and gives the threat actor the ability to disperse different payloads.
Among them is GootBot, which sends out beacons to its C2 server once every 60 seconds to retrieve PowerShell tasks to be executed and sends back HTTP POST requests to the server with the results of the execution.
GootBot’s additional skills include reconnaissance and lateral movement, which let it efficiently increase the attack’s scope.
“The discovery of the Gootbot variant highlights the lengths to which attackers will go to evade detection and operate in stealth,” according to the investigators. “This shift in TTPs and tooling heightens the risk of successful post-exploitation stages, such as GootLoader-linked ransomware affiliate activity.”


